Using Microsoft Office for
Mac as a Relational Database
By Jim Gordon, co-author of Office 2011
for Mac All-in-One For Dummies.
Part 9 - Adjusting Query table
properties
You can set query table properties
when you first import data by clicking the Properties button
in the Return External Data to Microsoft Excel
dialog (see Part 7 of
this tutorial). In
Part 7 we accepted the default settings. In this part of the
tutorial we explore query table properties more fully.
The QueryTable properties dialogs have been improved for
Office 2016. The dialogs now look and work like their Excel
for Windows counterparts. Excel 2016 will be discussed first,
followed by Excel 2011.
EXCEL 2016
To display QueryTable properties, select a cell anywhere in
the QueryTable, then, on the Data Tab of the Ribbon,
choose Connections > Properties. The smaller button
on the Ribbon labeled Properties controls different
aspects of the QueryTable.
EXCEL 2011
Right-click in data > Convert to Range. Right-click in data
again > Data Range Properties
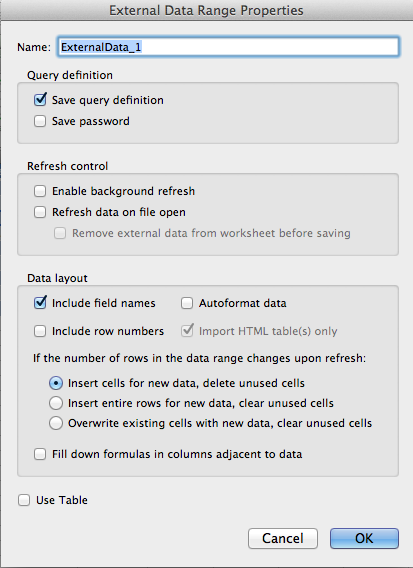
Name: You can name the query. This is not the name of
the table nor is it the name of the data range in which the
result set exists. The
name should be short, have no spaces or special characters and
should not conflict with other range or query names in your
workbook.
Query Definition:
- Save Query Definition.
If checked, the query is stored with the workbook and can
be refreshed and edited. If not checked, the query is not
stored in the query table or anywhere else.
- Save Password: If a
password was required to execute the query, check this box
to store password in the query table. Alternatively, you
can store a password in the DSN when you set it up in the
ODBC manager.
Refresh control: Discussed
in Part 8.
Data Layout: Choose options as desired. Checking the
box for AutoFormat data will cause Excel to
automatically re-size columns to fit the data,
Fill down formulas in columns adjacent to data: When
checked, you can use Excel's AutoFill feature to populate
adjoining columns based on cell formulas. See how this works
in Part 22.
Use Table: Check this box to display your data using an
Excel Table that can be formatted using options on the Table
tab of the Ribbon.
These properties can be adjusted using VBA.
Sub AdjustQueryTableProperties()
Range("A2").Select 'Select any cell in the
query table range
With Selection.QueryTable
.Name =
"ExternalData_1"
.UseListObject =
False
.FieldNames = True
.RowNumbers = False
.FillAdjacentFormulas = False
.HasAutoFormat =
False
.RefreshOnFileOpen
= True
.BackgroundQuery =
False
.RefreshStyle =
xlInsertDeleteCells
.SavePassword =
False
.SaveData = True
.TablesOnlyFromHTML
= True
End With
End Sub
Note: Most other query table properties found in the Windows
version of Office are not supported.
